The different physical systems are analogous to each other, if their differential equations are same.
The electrical system is analogous to hydraulic or mechanical system if their differential equations are same or behavioural characteristics are same.
In this case, the resistor is electrical component of the electrical system and it is analogous in hydraulic system by following example.
The resistor is used to oppose or limit the flow of current passing through the electrical circuit. Due to that, the voltage drop across resistor VR is generated in electrical system and pressure drop ∆P is generated in hydraulic system.
According to ohms laws,
Voltage drop in Volt = Current in Ampere * Resistor in Ohm ————- equation (1)
Similarly,
Pressure drop in KPa (Kilo Pascal) = Flow Rate in LPS (Litre Per Second) * Resistance (KPa/LPS) ————- equation (2)
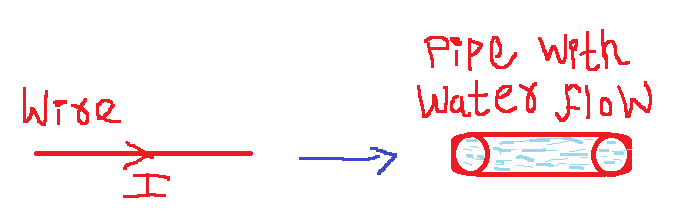
From fig. 1,
for electric circuit, the resistance of wire is 0.23 ohm.
If current flowing through this wire is 0 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 0 Volt.
If current flowing through this wire is 1 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 0.23 Volt.
If current flowing through this wire is 2 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 0.46 Volt.
If current flowing through this wire is 5 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 1.15 Volt.
Similarly, for hydraulic system, assume the resistance of the pipe is 1 KPa/LPS
If flow rate through this pipe is 0 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 0 KPa.
If flow rate through this pipe is 1 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 1 KPa.
If flow rate through this pipe is 2 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 2 KPa.
If flow rate through this pipe is 3 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 3 KPa.
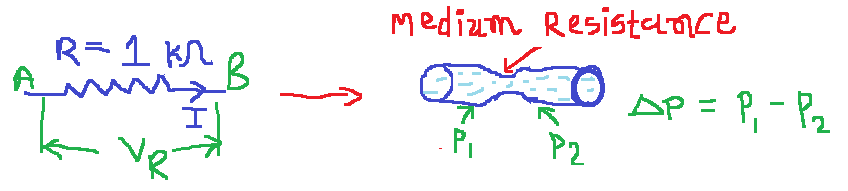
From fig. 2,
for electric circuit, the resistance of wire is 1kohm = 1000 ohm.
If current flowing through this wire is 0 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 0 Volt.
If current flowing through this wire is 0.00023 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 0.23 Volt.
If current flowing through this wire is 0.00046 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 0.46 Volt.
If current flowing through this wire is 0.00115 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 1.15 Volt.
Similarly, for hydraulic system, assume the resistance of the pipe is 10 KPa/LPS
If flow rate through this pipe is 0 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 0 KPa.
If flow rate through this pipe is 1 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 10 KPa.
If flow rate through this pipe is 2 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 20 KPa.
If flow rate through this pipe is 3 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 30 KPa.

From fig. 3,
for electric circuit, the resistance of wire is 100kohm = 100000 ohm.
If current flowing through this wire is 0 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 0 Volt.
If current flowing through this wire is 0.0000023 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 0.23 Volt.
If current flowing through this wire is 0.0000046 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 0.46 Volt.
If current flowing through this wire is 0.0000115 Ampere then the voltage drop is equal to 1.15 Volt.
Similarly, for hydraulic system, assume the resistance of the pipe is 100 KPa/LPS
If flow rate through this pipe is 0 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 0 KPa.
If flow rate through this pipe is 1 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 100 KPa.
If flow rate through this pipe is 2 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 200 KPa.
If flow rate through this pipe is 3 LPS then the pressure drop across pipe is equal to 300 KPa.
We conclude that, in electrical and hydraulic analogous system, the current is analogous to flow rate and the voltage is analogous to pressure.


 Users Today : 0
Users Today : 0 Total Users : 17795
Total Users : 17795 Views Today :
Views Today :