The Resistor is a passive type electrical component used in electric circuits to oppose or limit the flow of electric current.
The passive components require an external electrical supply, for its operation or the passive components not generate energy by themselves.
The properties of resistor, to limit the flow of current is known as the resistance and it is denoted by R.
The unit of resistance is ohm and symbolically the unit is represented by Ω.
The symbolic representation of resistor is shown below.

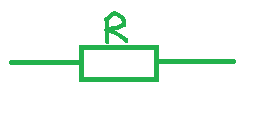
Now, As per ohm’s law. The electrical resistance R is equal to the ratio of the voltage V and the current I. The unit for voltage and current is volt and ampere respectively.
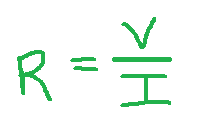
Now, discuss with example,
In an electrical circuit as shown in fig. 3, the current following it is 1.5 A and the battery connected to the circuit is 10 V. Find the value of the resistor in the fig. 3.
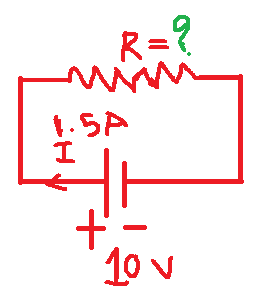
We know that,
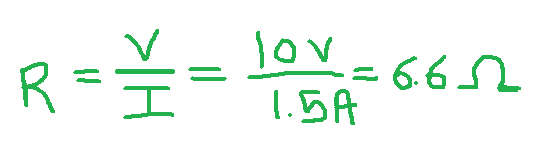
Now, the Voltage vs Current i.e. V-I Characteristics of Resistor:
In V-I Characteristics, on the x-axis and the y-axis the voltage and the current is presented respectively.
The V-I plot is drawn with respect to different constant value of resistor, 0 to 10 volt voltage and current value.
CASE NO.:- 1: R =1Ω, V = 1 to 10 V
| Voltage V | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Current A | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
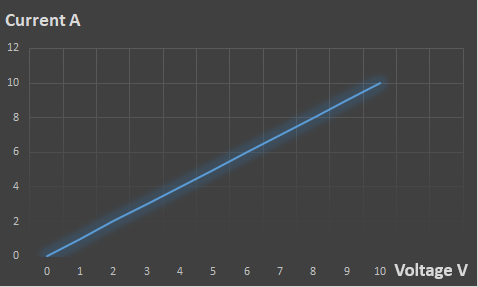
In the first case, when the voltage is increase from 0 to 10 V, the current is also increase from 0 to 10 A respectively as shown in fig. 4. That indicate the resistor is linear element. When voltage is decrease from 10 V to 0 V, the current is linearly decrease from 10 A to 0 A.
CASE NO.:- 2: R =10Ω, V = 1 to 10 V
| Voltage V | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Current A | 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 |
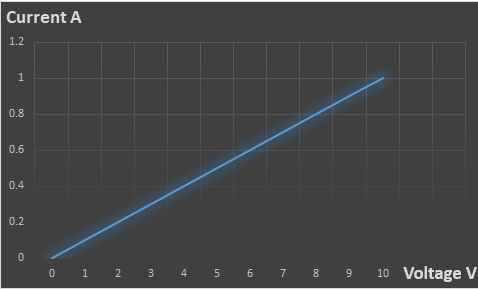
In the second case, when the voltage is increase from 0 to 10 V, the current is also increase from 0 to 1 A respectively as shown in fig. 5. That indicate the resistor is linear element. When voltage is decrease from 10 V to 0 V, the current is linearly decrease from 1 A to 0 A.
CASE NO.:- 3: R =100Ω, V = 1 to 10 V
| Voltage V | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Current A | 0 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.1 |
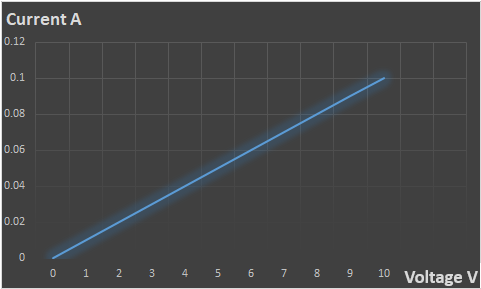
In the third case, when the voltage is increase from 0 to 10 V, the current is also increase from 0 to 0.1 A respectively as shown in fig. 6. That indicate the resistor is linear element. When voltage is decrease from 10 V to 0 V, the current is linearly decrease from 0.1 A to 0 A.


 Users Today : 1
Users Today : 1 Total Users : 17859
Total Users : 17859 Views Today : 1
Views Today : 1